Ever since the dawning of the information age, we’ve been talking about data, and its become the biggest commodity on the market. But for the translations industry, and more specifically for your projects, why is it so important to use your data effectively?
If your company has been exporting products and services for years, or even decades, you’ve undoubtedly had hundreds of documents translated into various languages. You may not realize it, but your back catalogue of translations may be a source of significant future savings for you!
How? With your previous translations, we can create a translation memory that will help reduce and optimize future translation costs. This is what we call aligning your files.
We’ll try to explain the procedure in more concrete terms
What is an alignment?
This is a process whereby we take a source document and its translation and ensure that each segment is properly correlated to its translation segment.
When we take these two files and add them to our CAT tool, it automatically aligns the segments based on segment position and translation length as below:
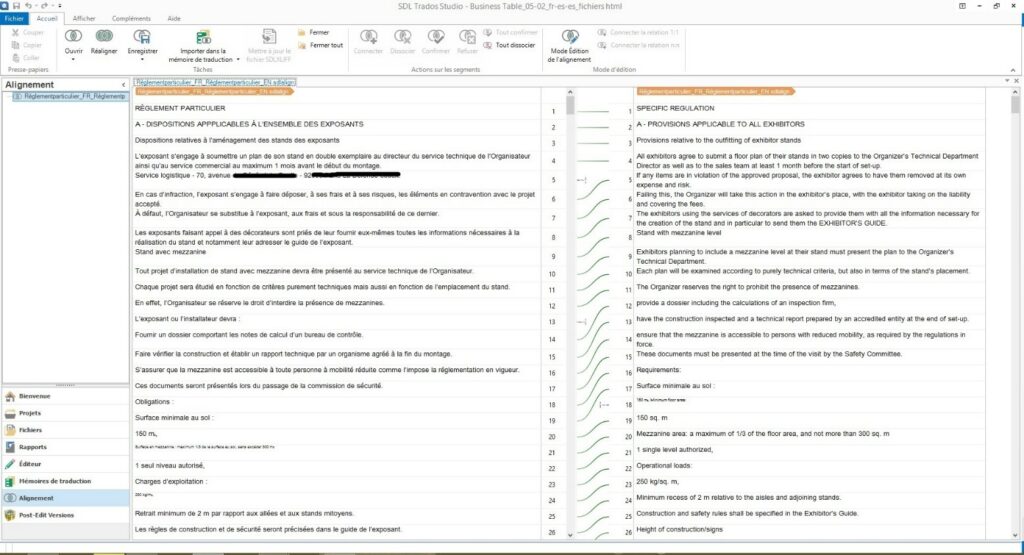
Translators must then manually verify that each proposed correlation is correct.
Why align your translations?
Running an alignment allows you to turn existing translations into translation segments that can be added to a database commonly referred to as a “translation memory” in order to create the memory, expand it, or update it.
After this, the translation can be used for future projects.
You thus gain in both cost and quality!
The price on invoices will be optimized because we will be able to reuse previously translated content to minimize the time demanded of our translators.
However, it is imperative that you send us only those translations where you have verified the quality as we do not correct the text during alignment. It would be entirely too time consuming and thus costly.
You’ll also be helping to improve the overall quality of your translations. Using a memory helps ensure your preferred terminology is maintained from one project to the next. The implementation of a glossary can also contribute to this improvement.
An alignment allows a translator to gain time while translating a new project. In concrete terms, how does it help them?
The translation will be recycled and suggested by the translation memory if the document they are currently translating contains a similar segment or exactly the same segment as one previously translated. The translator won’t be required to type it out again, simply proofread it and modify as necessary.
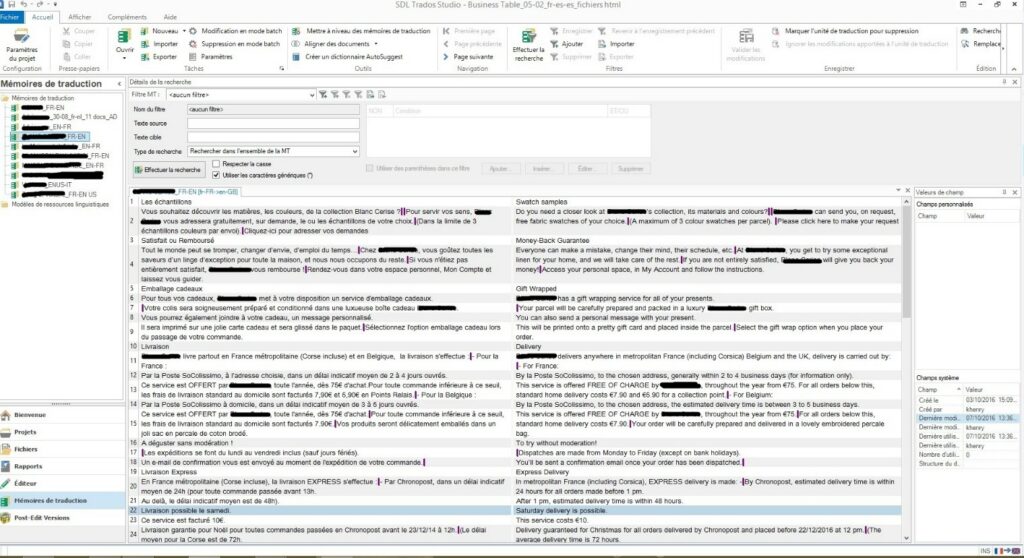
Below, you can see a screen capture of our translator’s view inside memoq while translating a file:
How do we get started?
We use our translation tools (memoQ ou Studio). The source and translations files are placed side-by-side. The translator verifies each segment, one at a time. Once each source segment is aligned with its corresponding translation, we export the segments to create, enhance, or update our translation memory database.
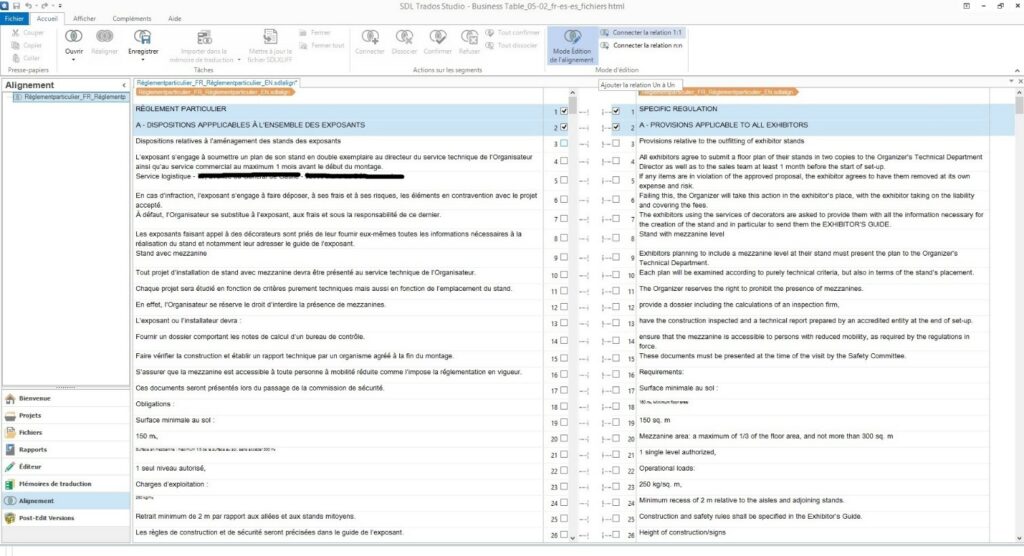
Adjusting the alignment of translation units
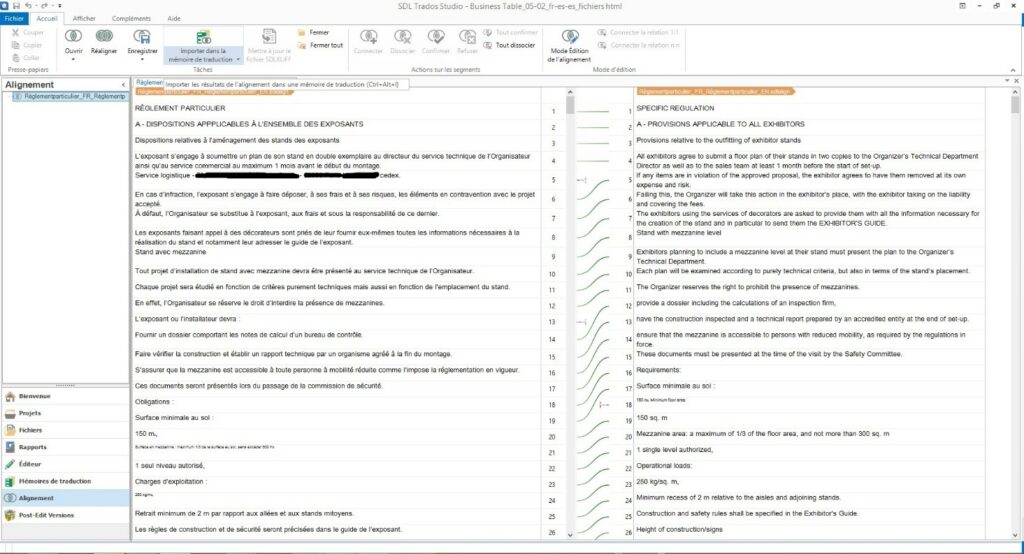
Validated segments ready to be exported to the translation memory
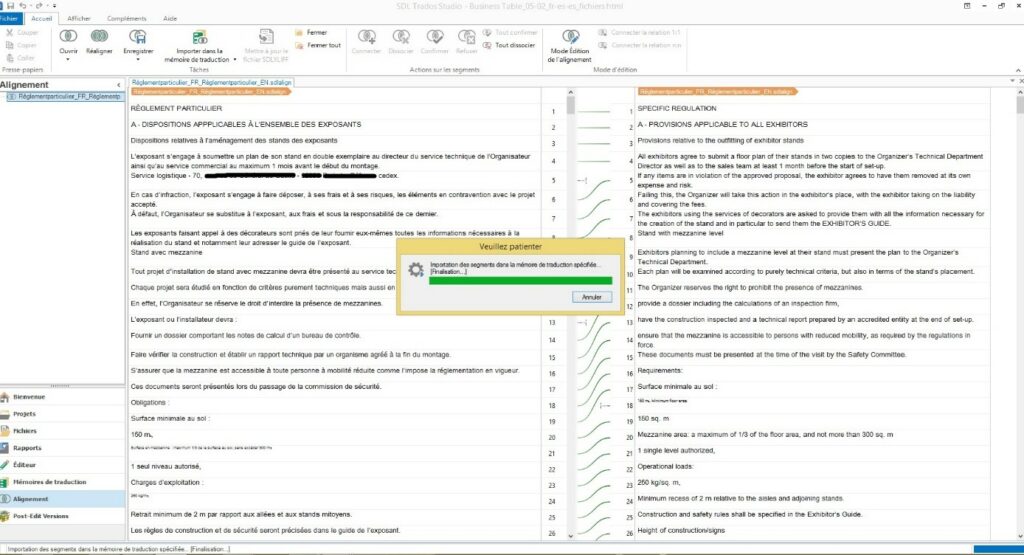
Importing to translation memory
What are the various kinds of alignments?
Alignment without verification to create a translation memory:
Sometimes the files to be reused can be extremely voluminous and in these circumstances, we may decide, with the client, to not move forward with the alignment, but rather to use these resources as reference documents.
In this case, we won’t create a translation memory from your documents (there’s too much risk of error) and the percentage of repetitions between your past translations and current project will be more limited. However, this may yet be an interesting option from a financial standpoint, especially if the source and target translation are provided in the same format and segmented in the same way.
The alignment will be carried out automatically without further verification.
The example below highlights the limitations of unverified alignments, as one single segment may throw a wrench in the works of the entire alignment:
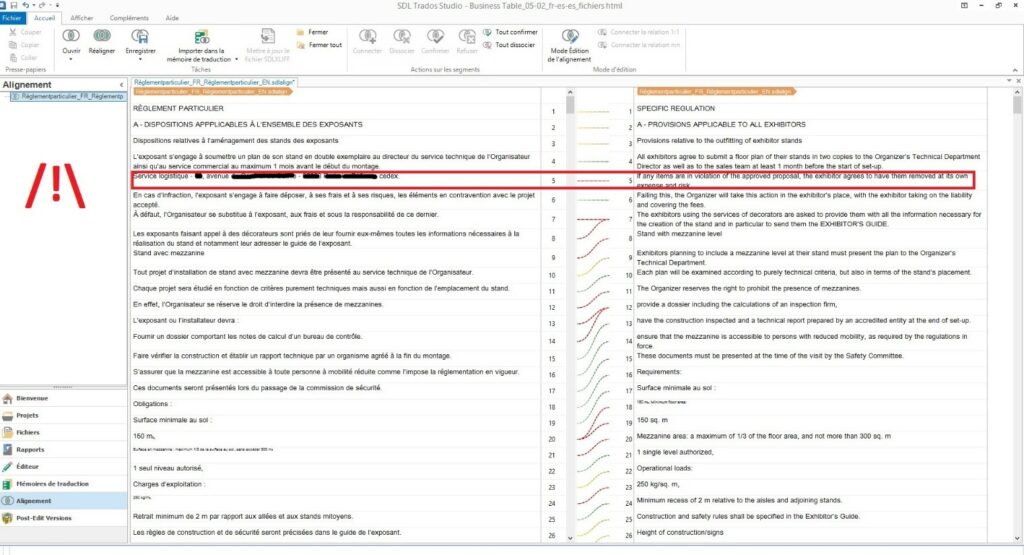
Alignment with verification:
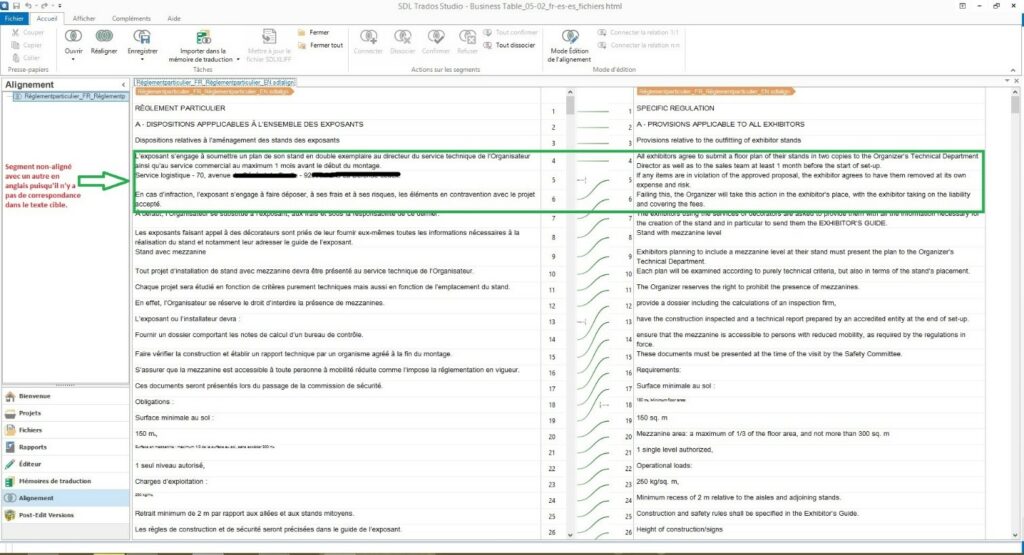
If you are aware of content that has been added to the target translation, or that has been ommitted from it, it will be immediately necessary to ensure human verification of your alignment.
In these such occassions, the translator will verify each source and target segment, manually re-aligning the correspondences as necessary.
Once the seg;ents are validated, they are imported into the translation memory. Depending on the specific request of the client, they will be considered as 100% exact repetitions for future projects, or as partial repetitions (99%) if the client believes they must be verified due to the changing context of the project. In this second case, the project manager will apply a percentage penalty when importing the segments to the translation memory.
Note that is also possible to create multiple translation memories from your content depending on the nature of the source material. With this in mind, you can create a “legal” translation memory, as well as a “technical” one, ore even a “marketing” memory with terms translated differently depending on the context of the project.
If you’re still left scratching you head about the process, take a moment to reach out and we can discuss the various issues at stake with reusing your past translated content as well as the use of unique translation memories for your business!
Depending on the context and your project, we can even provide the memory on the house 🙂

